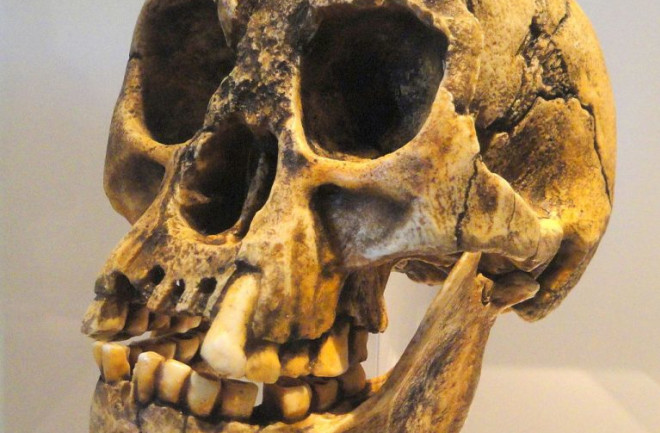
60,000 years ago, diminutive beings dwelled on the Indonesian island of Flores, alongside komodo dragons, pygmy stegodons and real-life rodents of unusual size. The now-extinct humans — known scientifically as Homo floresiensis, and popularly as the hobbits — stood less than 4 feet tall, with brains one third the size of living people. Yet, they made stone tools, butchered meat and somehow crossed miles of ocean to colonize their tropical home.
It’s been 15 years since researchers first announced H. floresiensis. The discovery astonished anthropologists worldwide — and called for immediate revision of the standard account of human evolution. Over the years, we’ve learned more about the species’ appearance, habits and time on Earth. But the hobbits’ origin and fate still remain a mystery.